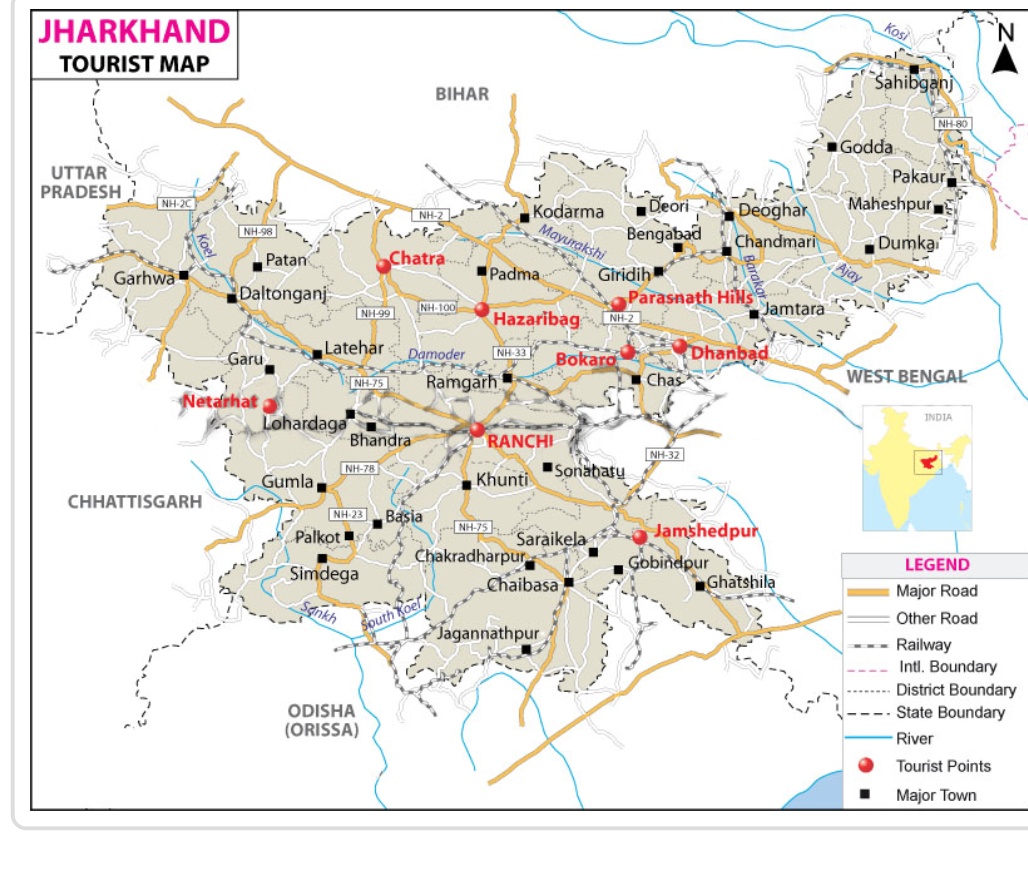
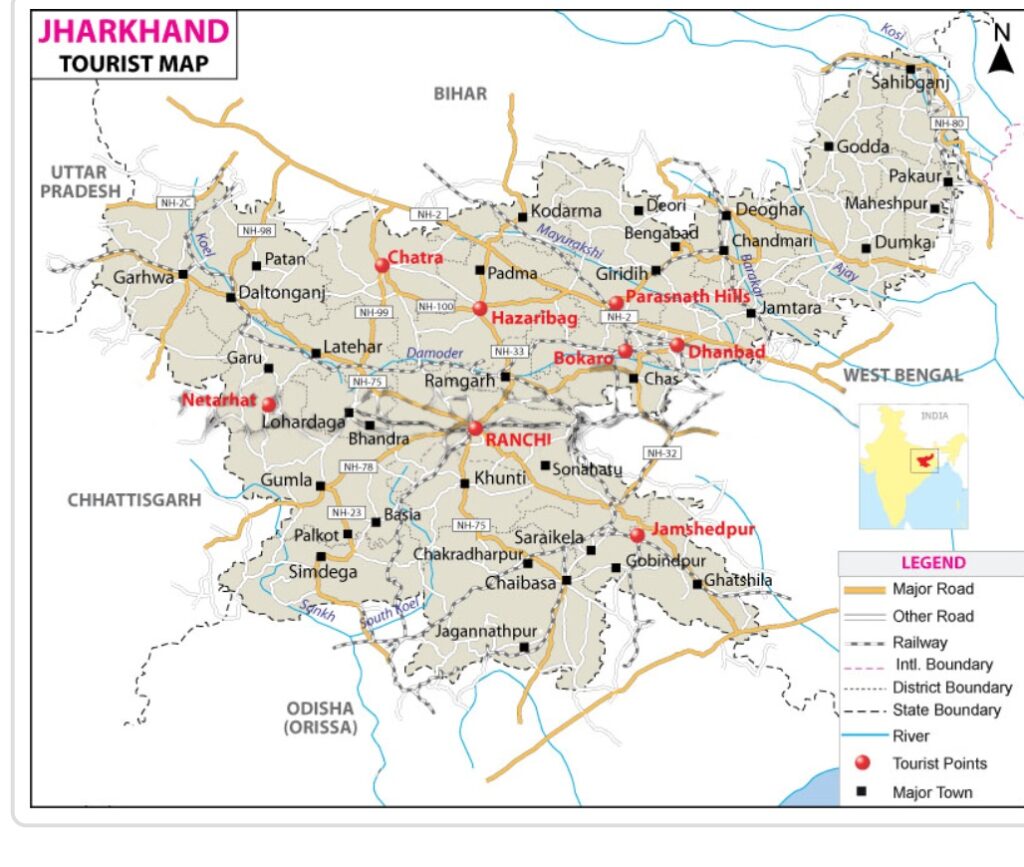
Jharkhand, a state in eastern India, is home to several wildlife sanctuaries that protect its rich biodiversity. Some of the prominent wildlife sanctuaries in Jharkhand include:
- Forest Cover: Jharkhand boasts a significant forest cover, covering approximately 29% of the state’s total land area. The state is home to a diverse range of forests, including tropical, sub-tropical, and deciduous forests.
- Biodiversity: The forests of Jharkhand are known for their rich biodiversity, with a variety of flora and fauna species. The state is home to several wildlife sanctuaries and national parks, such as Betla National Park, Hazaribagh Wildlife Sanctuary, and Palamau Tiger Reserve, where you can find a wide range of wildlife including tigers, leopards, elephants, deer, and various bird species.
- Forest Types: Jharkhand’s forests can be broadly categorized into several types, including tropical moist deciduous forests, tropical dry deciduous forests, and miscellaneous forests. These forests vary in terms of tree species and density.
- Important Tree Species: Some of the important tree species found in Jharkhand’s forests include sal (Shorea robusta), teak, bamboo, mahua, kendu, and semal. Sal is particularly abundant and commercially valuable.
- Tribal Communities: Jharkhand is home to various indigenous tribal communities who have a deep connection with the forests. These communities often rely on the forests for their livelihoods and have traditional knowledge of forest management and conservation.
- Forest Conservation Efforts: The government of Jharkhand, along with various environmental organizations, has been involved in several initiatives to protect and conserve the state’s forests. These efforts include afforestation programs, anti-poaching measures, and community-based conservation projects.
- Forest Threats: Like many other regions, Jharkhand’s forests face threats such as deforestation, illegal logging, encroachment, and habitat fragmentation. These threats can have a detrimental impact on the state’s rich biodiversity.
- Forest Department: The Jharkhand Forest Department is responsible for the management and conservation of the state’s forests. They work towards safeguarding the forests and promoting sustainable forest management practices.
- Eco-Tourism: Jharkhand’s forests also offer opportunities for eco-tourism and wildlife enthusiasts. Several eco-tourism destinations and trekking trails have been developed to promote tourism while ensuring the conservation of natural resources.
It’s important to note that the information provided here is based on my knowledge up to September 2021, and there may have been developments or changes since then. For the most up-to-date information on Jharkhand’s forests and conservation efforts, it is advisable to refer to official government sources and environmental organizations operating in the region.Wildlife Sanctuaries In Jharkhand
-
Palamau Tiger Reserve: Located in the Palamau district, this is one of the most significant tiger reserves in the state. It covers an area of around 1,129 square kilometers and provides habitat to a variety of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, elephants, and several species of deer.
-
Betla National Park: Situated in the Latehar district, Betla National Park is known for its diverse flora and fauna. It is home to tigers, leopards, sloth bears, elephants, and various species of birds. The park offers opportunities for nature lovers and wildlife enthusiasts to explore its beauty.
-
Dalma Wildlife Sanctuary: Located near Jamshedpur in the Dalma Hills, this sanctuary is known for its population of Indian bison (gaur). Other animals found here include elephants, leopards, sambar deer, and various bird species. The sanctuary is also famous for its beautiful landscapes.
-
Hazaribagh Wildlife Sanctuary: Situated in the Hazaribagh district, this sanctuary is known for its stunning scenery and diverse wildlife. You can spot animals like leopards, sambars, spotted deer, wild boars, and many bird species here.
-
Koderma Wildlife Sanctuary: Located in the Koderma district, this sanctuary is home to a variety of wildlife, including leopards, barking deer, sloth bears, and various bird species. It’s a lesser-known sanctuary but offers a peaceful environment for nature lovers.
-
Lawalong Wildlife Sanctuary: This sanctuary is located in the Chatra district and is known for its pristine natural beauty and diverse wildlife. It provides habitat to animals like tigers, leopards, elephants, and numerous bird species.
These wildlife sanctuaries in Jharkhand offer a glimpse into the state’s natural heritage and are essential for the conservation of its flora and fauna. Visitors can enjoy safaris and trekking in some of these sanctuaries while witnessing the beauty of the region’s wildlife and landscape
Jharkhand is a state located in eastern India, and it is known for its rich forest cover and biodiversity. Here are some details about the forests in Jharkhand:
- Forest Cover: Jharkhand boasts a significant forest cover, covering approximately 29% of the state’s total land area. The state is home to a diverse range of forests, including tropical, sub-tropical, and deciduous forests.
- Biodiversity: The forests of Jharkhand are known for their rich biodiversity, with a variety of flora and fauna species. The state is home to several wildlife sanctuaries and national parks, such as Betla National Park, Hazaribagh Wildlife Sanctuary, and Palamau Tiger Reserve, where you can find a wide range of wildlife including tigers, leopards, elephants, deer, and various bird species.
- Forest Types: Jharkhand’s forests can be broadly categorized into several types, including tropical moist deciduous forests, tropical dry deciduous forests, and miscellaneous forests. These forests vary in terms of tree species and density.
- Important Tree Species: Some of the important tree species found in Jharkhand’s forests include sal (Shorea robusta), teak, bamboo, mahua, kendu, and semal. Sal is particularly abundant and commercially valuable.
- Tribal Communities: Jharkhand is home to various indigenous tribal communities who have a deep connection with the forests. These communities often rely on the forests for their livelihoods and have traditional knowledge of forest management and conservation.
- Forest Conservation Efforts: The government of Jharkhand, along with various environmental organizations, has been involved in several initiatives to protect and conserve the state’s forests. These efforts include afforestation programs, anti-poaching measures, and community-based conservation projects.
- Forest Threats: Like many other regions, Jharkhand’s forests face threats such as deforestation, illegal logging, encroachment, and habitat fragmentation. These threats can have a detrimental impact on the state’s rich biodiversity.
- Forest Department: The Jharkhand Forest Department is responsible for the management and conservation of the state’s forests. They work towards safeguarding the forests and promoting sustainable forest management practices.
- Eco-Tourism: Jharkhand’s forests also offer opportunities for eco-tourism and wildlife enthusiasts. Several eco-tourism destinations and trekking trails have been developed to promote tourism while ensuring the conservation of natural resources.
It’s important to note that the information provided here is based on my knowledge up to September 2021, and there may have been developments or changes since then. For the most up-to-date information on Jharkhand’s forests and conservation efforts, it is advisable to refer to official government sources and environmental organizations operating in the region.